Roll cooling plays a critical role in optimizing the performance and efficiency of manufacturing processes, particularly in industries such as steel rolling, paper production, and metalworking. This article explores the concept of roll cooling, its applications, benefits, and the technologies behind it. Through understanding how effective roll cooling systems function, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, improved product quality, and better energy efficiency.
What is Roll Cooling?
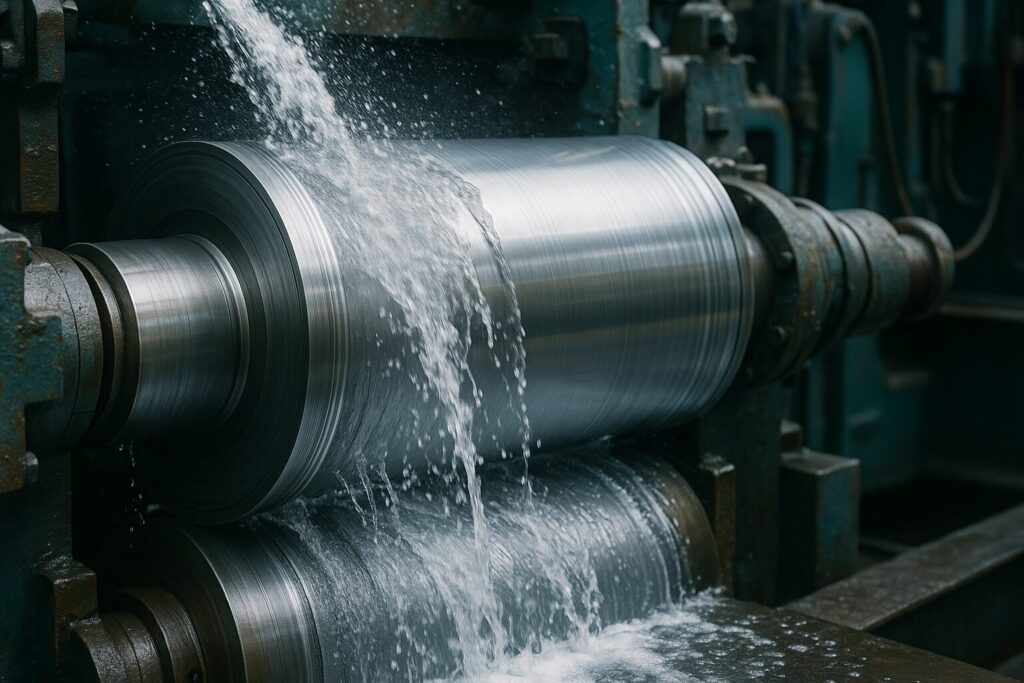
Roll cooling refers to the method used to cool the surface of rollers during industrial processes. These rollers are used to shape or process materials such as metal, paper, or plastic. As the material passes through these rollers, friction and heat are generated, leading to wear and tear if not properly managed. Roll cooling systems are designed to apply a controlled amount of coolant to the surface of the rollers to dissipate this heat, ensuring optimal operation and preventing damage.
In many industrial applications, roll cooling is vital for maintaining precise control over the temperature of the material being processed. By ensuring that the rollers stay at an appropriate temperature, manufacturers can prevent defects, improve efficiency, and extend the life of equipment. Roll cooling, therefore, is an integral part of the production line, offering benefits that go far beyond simply reducing temperatures.
The Role of Roll Cooling in Steel Rolling
Steel rolling is one of the most prominent applications of rolling cooling. In this process, large slabs of steel are passed through a series of rollers to shape them into thinner sheets. The intense pressure and friction involved in this process generate significant heat, which can distort the steel if not controlled properly. Roll cooling systems are used to regulate the temperature of the rollers, ensuring that the steel is processed uniformly.
Without effective roll cooling, the risk of thermal damage to the steel increases, which can lead to defects such as warping, cracking, or even roller wear. By applying coolants, often in the form of water or oil-based solutions, manufacturers can maintain a consistent temperature on the rollers, reducing the likelihood of such issues. This also helps improve the final product’s quality by ensuring that it is free from defects caused by overheating.
Advantages of Effective Roll Cooling Systems
1. Improved Product Quality
One of the primary benefits of roll cooling is the improvement in the overall quality of the finished product. In industries like steel and paper manufacturing, temperature control is crucial to avoid material defects. Excessive heat can lead to warping or irregular thickness, which can negatively affect the product’s strength, durability, and surface finish. Effective roll cooling ensures uniform temperature distribution, leading to higher-quality products.
2. Increased Production Efficiency
Roll cooling systems help prevent overheating, which can cause delays or interruptions in the production process. By maintaining the temperature within an optimal range, these systems ensure that the production line runs smoothly. This, in turn, leads to higher throughput and reduced downtime, improving overall production efficiency.
3. Extended Equipment Life
The high temperatures generated during rolling processes can cause wear and tear on the rollers. This results in increased maintenance costs and the need for frequent replacements. With proper roll cooling, the temperature of the rollers is kept within a safe range, reducing the risk of damage and extending their lifespan. This leads to lower maintenance costs and fewer interruptions to the production process.
4. Energy Efficiency
Managing heat effectively is not only important for the quality of the product but also for energy consumption. Roll cooling systems that use water or other cooling agents help dissipate heat in an energy-efficient manner. This reduces the need for excessive amounts of energy to maintain the desired temperature, contributing to lower operational costs and improved energy efficiency.
Technologies Behind Roll Cooling Systems
Several technologies are used to optimize roll cooling processes. Depending on the type of material being processed, the cooling system may vary, but all share the same fundamental purpose: to maintain consistent temperature control. Let’s take a closer look at the key technologies used in roll cooling.
1. Water-based Cooling Systems
Water is one of the most common coolants used in roll cooling systems due to its high thermal conductivity and availability. Water-based cooling systems can be applied in various forms, including direct jet cooling, where high-pressure water jets are aimed at the roller surface, or through spray systems that evenly distribute water across the roller surface. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, provided that proper filtration and treatment systems are in place to prevent water contamination.
2. Oil-based Cooling Systems
In some applications, oil is preferred over water as a coolant. Oil-based systems are typically used in industries where a more controlled cooling process is required, such as in the production of high-quality steel or other metals. Oils can provide better lubrication and prevent rust formation, making them an ideal choice in specific industrial environments. These systems can be more expensive than water-based systems but offer more precise temperature control and longer-lasting lubrication.
3. Air Cooling Systems
Air cooling systems are typically used in applications where cooling demands are less intense. These systems use fans or blowers to circulate air around the rollers, dissipating heat more slowly than liquid-based systems. While air cooling may not be as effective as water or oil systems in high-heat applications, it can be an energy-efficient solution for low-temperature processes.
4. Hybrid Cooling Systems
In some cases, hybrid systems that combine both liquid and air cooling technologies are used. These systems are designed to offer a balance between cooling performance and energy efficiency, adapting to varying production demands. Hybrid systems are ideal for industries where cooling requirements fluctuate based on the material being processed or the speed of the production line.
Challenges in Roll Cooling
While roll cooling systems offer many benefits, they also come with certain challenges. The effectiveness of these systems depends heavily on proper design, maintenance, and operation. Some of the common challenges associated with roll cooling include:
1. Clogging and Maintenance
Over time, coolants can accumulate debris or impurities that clog the cooling channels, reducing the effectiveness of the system. Regular cleaning and maintenance are required to keep the system running smoothly and ensure that the rollers stay properly cooled. This can lead to additional operational costs and downtime.
2. Environmental Concerns
The use of water or oil as coolants raises environmental concerns, particularly with regard to wastewater disposal. If not properly managed, coolant systems can contribute to pollution, which can result in fines or other regulatory issues. Implementing water treatment systems and ensuring proper disposal of waste products are essential to mitigating these risks.
3. Cost of Installation and Operation
While roll cooling systems can save money in the long run by improving product quality and equipment longevity, the initial installation costs can be high. Additionally, ongoing energy costs, especially for oil-based systems, can contribute to overall operational expenses. However, the long-term benefits typically outweigh these costs, especially for industries where precision and efficiency are paramount.
The Future of Roll Cooling
As technology continues to advance, so does the development of roll cooling systems. One promising area of innovation is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies can be used to monitor and adjust cooling parameters in real-time, ensuring that the system operates at peak efficiency.
In addition, more sustainable cooling solutions are being explored. With growing concerns about environmental impact, the development of eco-friendly coolants and energy-efficient cooling technologies is a priority for many manufacturers. As these systems evolve, roll cooling will continue to play a vital role in improving the sustainability and efficiency of industrial manufacturing.
Conclusion
Roll cooling is a vital aspect of industrial processes, particularly in metalworking, paper production, and other manufacturing sectors. By regulating the temperature of rollers during production, roll cooling systems help improve product quality, increase efficiency, and extend equipment life. As technology advances, roll cooling systems are becoming more sophisticated and energy-efficient, offering manufacturers the ability to optimize their processes even further. Understanding and investing in effective roll cooling technologies is essential for any industry looking to maintain high-quality production and reduce operational costs.