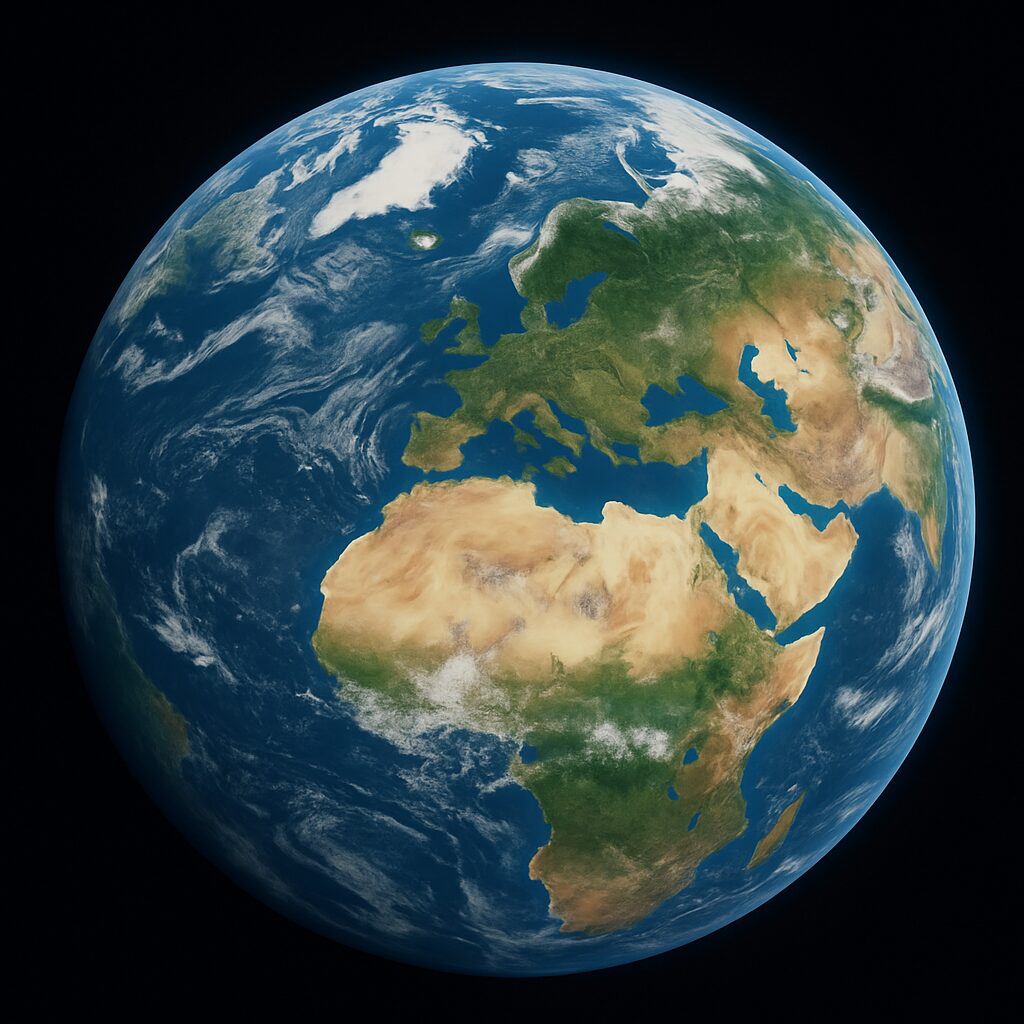
In an age where satellite imagery and 3D visualization technology are transforming how we perceive the world, earthview 3d maps stand out as an essential tool. These advanced mapping platforms merge high-resolution satellite images with three-dimensional perspectives, offering an interactive experience that brings geography to life.
What Are Earthview 3D Maps?
These platforms combine satellite imaging and geographic data to create three-dimensional views of terrains, landmarks, and urban environments. They are widely used in various sectors such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, real estate, and education. The term “3D” indicates the incorporation of elevation, depth, and perspective, allowing users to see features as if they were physically present.
Evolution of 3D Mapping Technology
3D mapping has evolved significantly over the past decade. Early attempts involved rudimentary modeling techniques and flat renderings. However, technological advancements in LiDAR, satellite imaging, and computational modeling have revolutionized the industry. Companies like Google, Apple, and independent developers have invested heavily in refining these tools, resulting in higher accuracy and realism.
Key Features of 3D Mapping Platforms
- High-Resolution Imagery: Captured via satellite and aerial photography, providing stunning visual clarity.
- Terrain Elevation: Displays natural formations like mountains, valleys, and riverbeds in their real dimensions.
- Interactive Navigation: Users can zoom, pan, rotate, and tilt the map to explore different angles.
- Landmark Detailing: Accurately renders iconic buildings and infrastructure.
- Layer Integration: Users can overlay traffic, weather, or demographic data onto the 3D maps.
Applications in Urban Planning
City planners and architects leverage 3D maps to visualize urban growth, simulate future developments, and assess environmental impact. These maps help decision-makers understand spatial relationships and optimize land use planning. Simulations of shadow casting, water flow, and population density all become easier and more insightful with 3D visualization.
Enhancing Environmental Monitoring
These maps play a vital role in environmental monitoring. Scientists can track deforestation, glacier retreat, and coastline changes over time using time-lapse features. The elevation and topography data support predictive modeling of natural disasters such as landslides, floods, and volcanic eruptions.
Revolutionizing Real Estate
In real estate, these maps allow buyers and developers to view properties in context. Potential homeowners can explore neighborhoods, assess proximity to amenities, and understand the topography before visiting the site. Developers can evaluate how a new construction will fit within the existing landscape.
Educational Benefits
Teachers and students benefit by exploring global geography, historical landmarks, and geological formations. The interactive nature of these maps makes learning more engaging and immersive. Geography lessons become virtual field trips, sparking curiosity and deeper understanding.
Integration with Augmented Reality
As AR technology continues to evolve, its integration opens new doors. Tourists can overlay 3D maps onto real-world views via smartphones or AR glasses. This capability enhances travel experiences, turning sightseeing into an educational and interactive journey.
Impact on Tourism and Travel
These platforms are transforming how tourists plan their travels. With detailed 3D previews of cities and natural wonders, travelers can create more informed itineraries. Travel agencies embed these maps on their platforms to offer virtual previews, enticing potential customers.
Military and Strategic Uses
Governments and defense agencies utilize 3D maps for strategic planning and reconnaissance. These platforms provide essential data for troop movement, base construction, and surveillance operations. Accurate terrain modeling enhances mission planning and reduces risks.
Improving Disaster Response and Relief
When natural disasters strike, rapid assessment is crucial. These tools enable emergency responders to evaluate damage, identify accessible routes, and coordinate aid distribution. Time-lapse features help compare before-and-after scenarios for efficient planning.
Role in Agriculture and Land Management
Farmers and land managers use these maps to monitor crop health, soil erosion, and water distribution. These insights lead to more sustainable agricultural practices. Precision farming becomes more feasible when combined with drone surveillance.
Mining and Geological Exploration
Geologists rely on these platforms to identify mineral deposits, assess fault lines, and map subterranean features. Mining companies use them to plan extraction routes, ensure safety, and minimize environmental impact. Advanced simulations support these operations.
Navigation and Transportation
Navigation apps are increasingly incorporating 3D features for more intuitive guidance. Drivers benefit from real-world views, while logistics companies use 3D data to optimize delivery routes and assess terrain challenges. Aviation and maritime navigation also gain from enhanced spatial awareness.
Smart Cities and IoT Integration
These tools are crucial components in the development of smart cities. They support the integration of IoT sensors, enabling real-time monitoring of infrastructure, traffic, and public utilities. These maps serve as the spatial framework for urban intelligence systems.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their many benefits, these platforms face challenges such as:
- Data Accuracy: Frequent updates are required to reflect ongoing changes.
- Privacy Concerns: High-resolution imagery raises surveillance and data privacy issues.
- Accessibility: Not all users have the devices or bandwidth required to view 3D content smoothly.
- Cost of Development: Creating and maintaining these maps demands significant resources.
Open Source and Community Projects
Several open-source projects contribute to the advancement of 3D mapping. Platforms like OpenStreetMap and CesiumJS offer tools for developers to build custom versions. Community-driven efforts ensure that mapping data remains accessible and customizable.
Corporate Players in 3D Mapping
Major tech companies continue to invest in these technologies:
- Google Earth: One of the pioneers in earthview 3d maps.
- Apple Maps: Offers high-detail Flyover views of major cities.
- Microsoft Bing Maps: Provides Streetside views and 3D cities.
- Here Technologies: Supplies maps for automotive and industrial uses.
Future Innovations
Looking forward, the future of 3D mapping is promising:
- AI Integration: Automates data processing and enhances map accuracy.
- Real-Time Updates: Drone and satellite networks will offer more frequent data refreshes.
- Holographic Displays: Emerging tech will allow users to view maps in 3D without screens.
- Virtual Reality: Entire cities and terrains can be explored via immersive VR environments.
Ethical Considerations
As these maps become more ubiquitous, ethical questions arise:
- Consent: Do individuals have a say in how their properties are represented?
- Bias: Ensuring equal mapping attention to underdeveloped regions.
- Surveillance: Balancing benefits with civil liberties.
Conclusion
Earthview 3D Maps represent a monumental leap in how we visualize and interact with our world. From urban planning to disaster response, their applications are diverse and impactful. As technology evolves, so too will the precision, usability, and reach of these tools. By using earthview 3d maps thoughtfully and ethically, we can unlock new dimensions in exploration, education, and decision-making.
Final Thoughts
As we stand on the brink of a more interconnected and visual future, earthview 3d maps serve as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds. Their value will only increase as we embrace smarter cities, real-time data, and immersive experiences. For users, developers, and policymakers alike, now is the time to harness the full potential of earthview 3d maps.